All you need to know about Real-time Rendering
In the ever-evolving world of 3D graphics, real-time rendering has become a transformative technology that connects creativity and interactivity. This article takes you through the definition of real-time rendering, explores its applications in the game industry, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR), and architectural visualization. You’ll also learn about its benefits, limitations, and some of the most famous real-time rendering software available today. Whether you’re a game developer, 3D artist, or architect, understanding real-time rendering helps you make informed choices about which rendering workflow best suits your creative needs.

Table of Contents
What is Real-Time Rendering?
Real-time rendering is a technique that enables you to generate 3D images or animations almost instantly using a render engine. This method allows users to interact with 3D scenes in real-time, providing immediate visual feedback for any adjustment made – such as changing lighting, textures, or camera angles.
Because it renders frames so quickly, real-time rendering relies heavily on powerful hardware, particularly high-performance GPUs. This is in contrast to traditional or offline rendering, where images are processed over a longer period and often result in higher-quality visuals. Offline rendering doesn’t demand such powerful machines but takes far more time to deliver the final output. Real-time rendering, therefore, prioritizes speed and interactivity over ultimate visual fidelity.
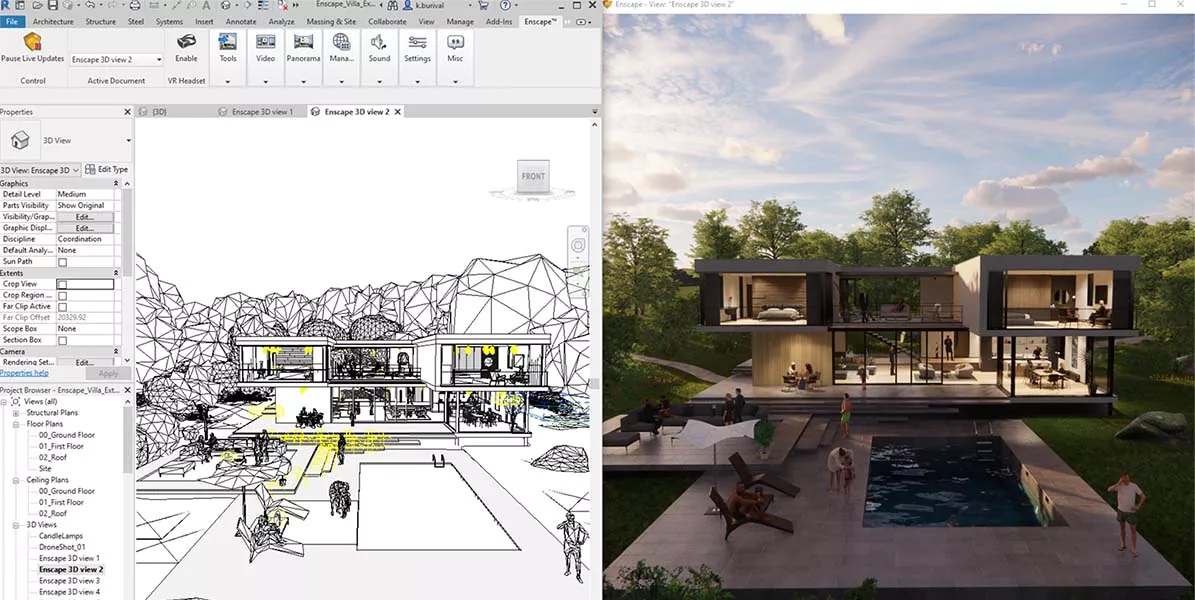
What is an Example of Real-Time Rendering?
Video games are the most well-known example of real-time rendering in action. Gamers can move through immersive 3D environments, interact with objects, and experience dynamic lighting and reflections, all while maintaining high frame rates (FPS). Everything that happens in the game world, from explosions to character animations, is rendered instantly as the player interacts with it. This instant feedback loop is what makes games feel alive and responsive.
In virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), real-time rendering plays an equally critical role. VR headsets demand incredibly low latency and high FPS to ensure a comfortable, immersive experience. The rendering engine must immediately respond to a user’s head or body movements, updating the visuals accordingly to avoid motion sickness. Similarly, AR applications overlay digital content onto the real world in real time, requiring precise rendering synchronization with live camera feeds.
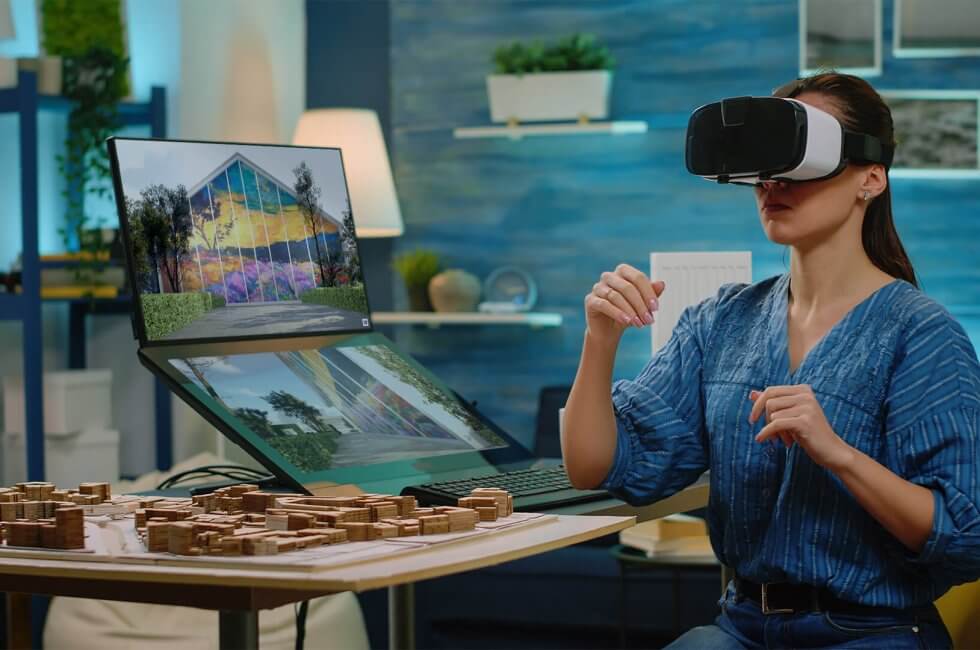

Real-time rendering has also gone into architectural visualization. With tools that allow interactive walk-through simulations, architects and clients can explore a building’s interior or exterior before it’s built. Users can adjust materials, lighting, and furniture arrangements in real time, helping designers make informed decisions faster and enhancing client presentations.
What Are the Benefits of Real-Time Rendering?
One of the biggest advantages of real-time rendering is its speed. Unlike offline rendering, where you might wait minutes or hours for a single frame, real-time rendering delivers visuals instantly. This allows 3D artists and studios to preview adjustments and design iterations immediately, greatly accelerating the creative process. The result is fast iteration and reduced production time, giving teams more room to refine and perfect their work.
Another benefit is that real-time rendering encourages experimentation. Since you can see your changes as you make them, you’re free to test different lighting setups, textures, materials, or visual effects without committing to lengthy render times. This flexibility makes it easier for artists to explore creative ideas, compare different moods, and decide what looks best before finalizing the scene.
Lastly, real-time rendering enables seamless interaction. This is especially important in interactive applications like video games or architectural walk-throughs, where users can freely navigate the 3D environment, zoom in or out, and adjust viewing angles – all while maintaining smooth performance and detailed visual feedback. It turns static 3D designs into engaging, dynamic experiences.
Are There Any Limitations of Real-Time Rendering?
Despite its advantages, real-time rendering does come with some limitations. The most significant challenge is that it requires powerful hardware. Achieving smooth, high-quality real-time visuals demands top-tier GPUs, fast CPUs, and sufficient memory, which can be expensive. For professionals aiming for high fidelity in large projects, this can become a substantial investment.
Another limitation is that most real-time rendering software runs on a single GPU, which can be a bottleneck for rendering performance. Unlike offline renderers that can leverage multiple GPUs or distributed rendering setups, real-time renderers are often restricted to a single device. This means scaling performance usually involves multiple single-GPU machines, increasing hardware and software licensing costs.
Finally, visual quality in real-time rendering is often less detailed than offline rendering. Because speed is prioritized, some effects like advanced global illumination, ray tracing accuracy, and ultra-high-resolution textures may be simplified or approximated. While modern engines are rapidly improving, offline rendering still holds the edge when it comes to photorealistic output.
Some Famous Real-Time Rendering Software
Unity is developed by Unity Technologies and is one of the most popular real-time rendering engines in the world. Widely used in the gaming industry, Unity is CPU-based and offers a flexible environment for both 2D and 3D game development. Its major strengths include an easy learning curve, cross-platform deployment, a massive asset store, and strong community support. Unity’s real-time lighting, physics, and scripting tools make it ideal for indie developers and small studios alike.
Unreal Engine, developed by Epic Games, is another industry-leading real-time rendering engine. Unlike Unity, Unreal primarily utilizes GPU rendering, delivering breathtaking graphics quality and realistic lighting through its Lumen and Nanite technologies. It’s heavily used in AAA game development, film production, and architectural visualization. Unreal Engine stands out for its cinematic-quality visuals, powerful blueprints system, and robust real-time ray tracing features.
Twinmotion, also developed by Epic Games, is tailored specifically for architectural visualization. It harnesses GPU power to produce real-time, high-quality visuals with minimal effort. Its strength lies in its user-friendly interface, allowing architects and designers to import models, adjust lighting, weather, and materials interactively. Twinmotion is favored for creating realistic animations and immersive VR presentations quickly.
Lumion, developed by Act-3D, is another popular GPU-based renderer for architects. Known for its simplicity and speed, Lumion allows users to transform CAD models into stunning, lifelike renders in minutes. It features an extensive content library of objects, people, plants, and weather effects, enabling professionals to visualize architectural designs in vibrant environments without needing deep technical expertise.
Enscape, developed by Chaos Group (formerly Enscape GmbH), is a real-time rendering and VR plugin integrated directly into popular modeling tools like Revit, SketchUp, Rhino, and ArchiCAD. It’s known for its smooth workflow and direct integration, allowing architects to visualize designs instantly without exporting models. Enscape is widely used for client presentations thanks to its interactive walkthroughs and live synchronization features.
Chaos Vantage, developed by Chaos Group, is designed for photorealistic real-time visualization using GPU rendering. It’s particularly optimized for V-Ray scenes, offering instant conversion from offline to real-time rendering without compromising on realism. Chaos Vantage excels in handling complex scenes with accurate lighting, reflections, and global illumination, making it a powerful companion tool for V-Ray users.
D5 Render, developed by Dimension 5, is a fast-growing real-time renderer built for architectural visualization. It utilizes GPU acceleration and supports ray tracing for high-quality results. D5 Render stands out with its intuitive UI, high-quality asset library, and real-time post-processing tools. It bridges the gap between ease of use and visual fidelity, making it a favorite among modern designers.
Conclusion
Real-time rendering is transforming how 3D artists, game developers, and architects bring their ideas to life. It allows creators to see effects, lighting, and materials instantly, eliminating long waits and encouraging experimentation and creativity. This immediacy leads to faster client feedback, more productive workflows, and greater artistic freedom. As technology advances, the 3D industry continues to embrace real-time rendering across multiple sectors, offering an ever-growing selection of powerful tools and engines. Whether you’re building virtual worlds, designing architecture, or exploring VR, real-time rendering opens the door to a more interactive and efficient creative future.
See more:







No comments