Octane Render Benchmark: How fast is your GPU?
If you are a 3D artist and want to know if your GPU is powerful and how it compares to others, you need to use rendering benchmarking tools. Octane Render Benchmark or OctaneBench is one such tool. It is a popular benchmark used to measure GPU performance with OctaneRender.
Whether you are building a new workstation, upgrading your GPU, or just curious about how your PC stacks up, OctaneBench is a great tool to help guide your decisions.
But what exactly does OctaneBench measure? How do you interpret the score? And what can you do to improve it? In this article, VFXRendering will walk you through everything you need to know about the Octane Render benchmark, from how it works to how to make the most of your results.

Table of Contents
Octane Render Benchmark
What is Octane Render Benchmark?
The Octane Render Benchmark, better known as OctaneBench, is a free benchmarking tool developed by OTOY, the developers of OctaneRender. It is designed to evaluate your computer’s GPU rendering performance by running a series of Octane scenes and settings and calculating how quickly your graphics card(s) can render them.
OctaneBench renders scenes on your hardware and then gives you a numerical score (OctaneBench Scores). The higher the score, the faster your PC can render in Octane, which means the more powerful it is. Octane Render Benchmark supports both single-GPU and multi-GPU configurations, so anyone can make use of it whether in personal laptops or studio setups.
Because Octane is a GPU-based renderer, the benchmark focuses exclusively on GPU performance, not including CPU, RAM, or disk speed. It is especially helpful for comparing different graphics cards or checking how well your multi-GPU system is scaling.
Understanding OctaneBench Scores
Once you run OctaneBench, you will get a score, maybe something like 100 or 1000. But what does that number really mean?
A higher score means faster rendering. It is a measure of how quickly your GPU(s) completed the test scenes. The benchmark uses the GeForce GTX 980 as a baseline, which scores 100. So, a card that scores 400 is roughly 4 times faster than a GTX 980.
OctaneBench scores of some GPUs:
- RTX 3090: 648 (average score)
- RTX 4090: 1271 (average score)
- The latest Geforce RTX 5090: 1720 (score received from Jules Urbach)
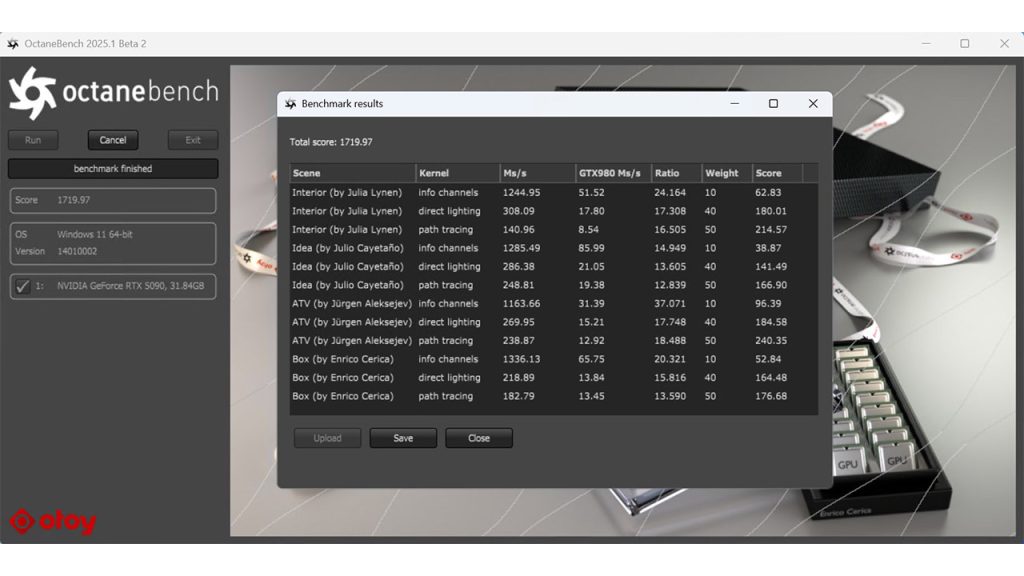
RTX 5090 benchmark result
Keep in mind that OctaneBench performance scales with GPU power, but also depends on other factors like VRAM size, cooling, driver versions, and whether your system is using multiple GPUs efficiently. If your score is significantly lower than expected for your GPU model, it could be a sign of driver issues, thermal throttling, or other performance bottlenecks.
OctaneBench Different Use Cases
When knowing the OctaneBench score of a GPU or multiple GPUs, you can base on it to buy or upgrade hardware for your PC.
Freelancers and Solo Artists
If you work on still frames or short animations, even a single GPU with a score of 600 – 1200 can handle most tasks smoothly.
- Recommendation: RTX 3080, 3090, or 4070 Ti.
Studios and Teams
For high-resolution rendering, heavy scenes, or frequent deadlines, workstations with multiple GPUs scoring 2000+ combined are ideal.
- Recommendation: RTX 4090, RTX 5090, and multiple GPU setups.
Using Render Farm
Octane Render Benchmark also has a use case in using a render farm. Render farms often offer a render farm cost calculator. We put the information about our project and OctaneBench score in this tool. Then it will estimate how long it will take to render on the farm compared to our local computer and how much it will cost as well.
Limitations of Octane Render Benchmark
While OctaneBench is a valuable tool, it is important to understand what it does not tell you.
- Not all workloads are the same: A higher score does not always guarantee faster performance in every project, especially if your scene involves complex materials, high poly counts, or large textures.
- No CPU or RAM testing: OctaneBench only measures GPU speed. It will not catch bottlenecks caused by slow CPUs, insufficient RAM, or storage limitations.
- Not reflect viewport performance: The benchmark is for final rendering only, it does not reflect real-time interaction in the 3D viewport.
- Thermal and power differences: Laptops or compact builds might throttle performance, giving lower scores even with the same GPU.
In short, OctaneBench is a great GPU rendering benchmark tool, but it is just one part of evaluating a full 3D rendering setup.
How to Improve Your Octane Render Benchmark Scores
You want to improve the performance of your computer. Here are a few tips to boost your OctaneBench score as well as your real rendering speed.
- Update your GPU Drivers: Always use the latest NVIDIA Studio Drivers if you are using NVIDIA cards.
- Improve cooling: If your GPU runs hot, it may throttle to avoid overheating. A better case fan setup or GPU cooler can help.
- Disable background tasks: Shut down browser tabs, heavy applications, or background services while benchmarking and, of course, rendering.
- Optimized system: Disable power-saving settings, and ensure your GPU is running at maximum performance mode in the NVIDIA Control Panel.
- Overclocking (consider carefully): Some users overclock their GPUs to push higher performance. This comes with risks, so research thoroughly and monitor temps.
How to Run an Octane Render Benchmark Test
OctaneBench Software
Until now, there have been 4 versions of OctaneBench software. They are:
- 1) OctaneBench® 2020.1
- 2) OctaneBench® 4.00c
- 3) OctaneBench® 3.06.2
- 4) OctaneBench® 2.17
The latest version also the version that is most used now, is OctaneBench® 2020.1.
The software is available for Windows, Linux, and Mac OSX. If you want to benchmark your own hardware, you can download OctaneBench here.
Requirements
The hardware and software requirements to run OctaneBench are the same as for OctaneRender Standalone.
- Latest CUDA® 10 drivers and a CUDA-enabled NVIDIA® video card with support for compute capability 3.0 or higher.
- A minimum of 8 GB RAM
- A fast multi-core CPU is not required, but it does significantly improve scene-loading speeds.
- Operating System: Windows® 7 or higher (64-bit), Linux® (64-bit), macOS® 10.13.6 High Sierra.
OctaneBench does not require an OctaneRender Standalone License to run.
How to Run an Octane Render Benchmark Test
Here are the steps to run an Octane render benchmark test:
1. Download the archive for your operating system.
2. Open the downloaded archive.
- Windows: Extract the archive into a directory of your choice and then open the extracted folder “OctaneBench_2020_1_5_win”.
- Linux: Extract the archive into a directory of your choice and then open the extracted folder “OctaneBench_2020_1_5_linux”.
- Mac OSX: You can copy the application “OctaneBench 2020.1.5” into the application folder or any other directory or just leave it in the .DMG image.
3. Run OctaneBench.
- Windows: Double-click “octane.exe” in the Windows Explorer.
- Linux: Run the binary “octane”.
- Mac OSX: Run “OctaneBench 2020.1.5”.
4. Choose if you want to benchmark with or without RTX enabled.
5. Enable the GPUs you want to benchmark.
6. Click “Run” and wait until the benchmark run has finished.
7. Marvel at the statistics, which you can then upload or save as a text / CSV file.
Octane Render Benchmark Comparison (2025 Update)
Let’s see the top OctaneBench results in the 2020.1 version.
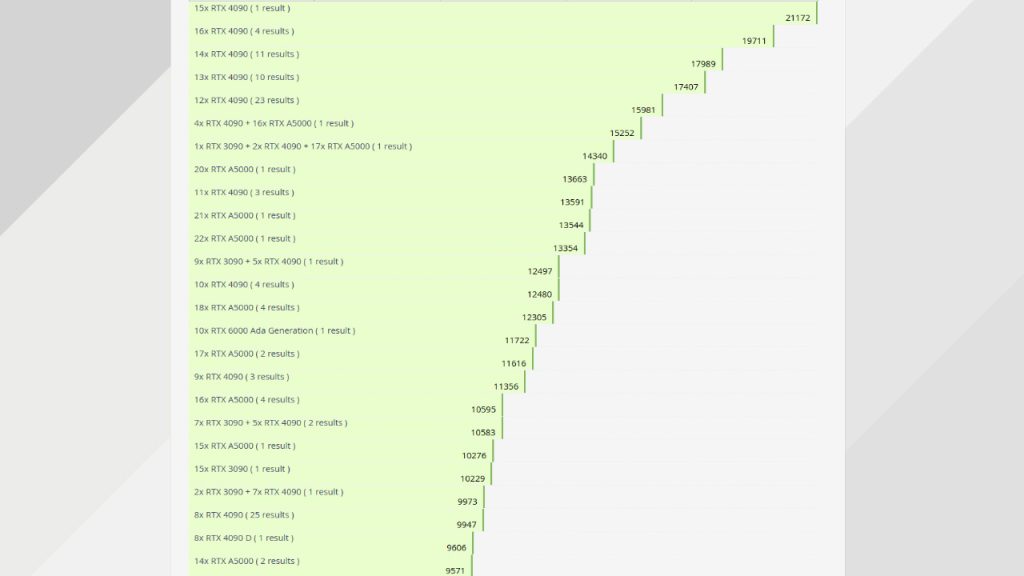
For those who are interested in RTX 3090, RTX 4090, and multi-GPU scaling, check out the tables below.
| RTX 3090 setups | OctaneBench scores |
| 1x RTX 3090 | 648 |
| 2x RTX 3090 | 1301 |
| 3x RTX 3090 | 1957 |
| 4x RTX 3090 | 2602 |
| 5x RTX 3090 | 3211 |
| 6x RTX 3090 | 3826 |
| 7x RTX 3090 | 4625 |
| 8x RTX 3090 | 5225 |
| 9x RTX 3090 | 5788 |
| 10x RTX 3090 | 6365 |
| 11x RTX 3090 | 6670 |
| 12x RTX 3090 | 6418 |
| 14x RTX 3090 | 9103 |
| 15x RTX 3090 | 10229 |
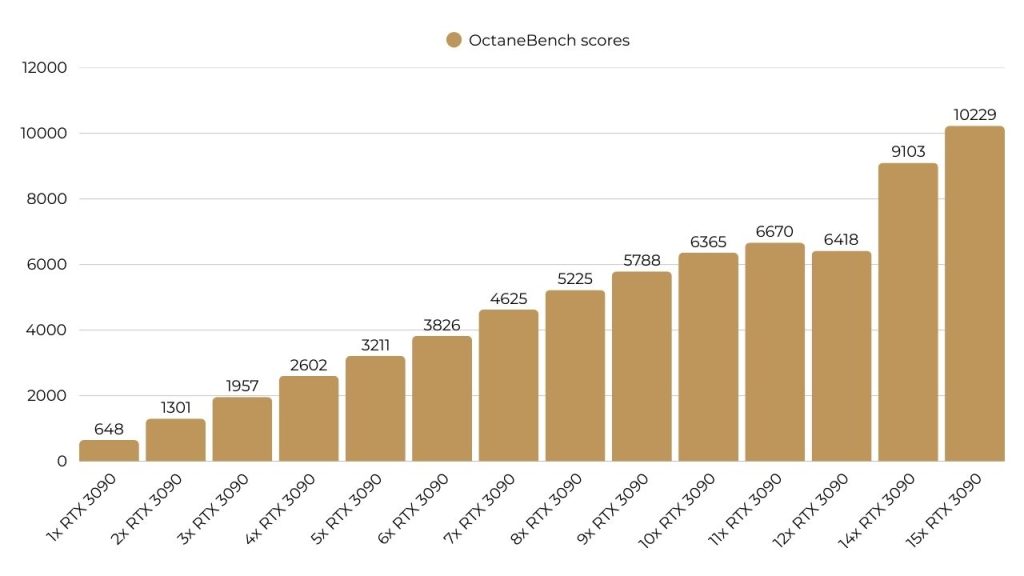
OctaneBench scores of single and multiple RTX 3090 setups
| RTX 4090 setups | OctaneBench scores |
| 1x RTX 4090 | 1271 |
| 2x RTX 4090 | 2529 |
| 3x RTX 4090 | 3530 |
| 4x RTX 4090 | 5132 |
| 5x RTX 4090 | 6334 |
| 6x RTX 4090 | 7508 |
| 7x RTX 4090 | 8875 |
| 8x RTX 4090 | 9947 |
| 9x RTX 4090 | 11356 |
| 10x RTX 4090 | 12480 |
| 11x RTX 4090 | 13591 |
| 12x RTX 4090 | 15981 |
| 13x RTX 4090 | 17407 |
| 14x RTX 4090 | 17989 |
| 15x RTX 4090 | 21172 |
| 16x RTX 4090 | 19711 |
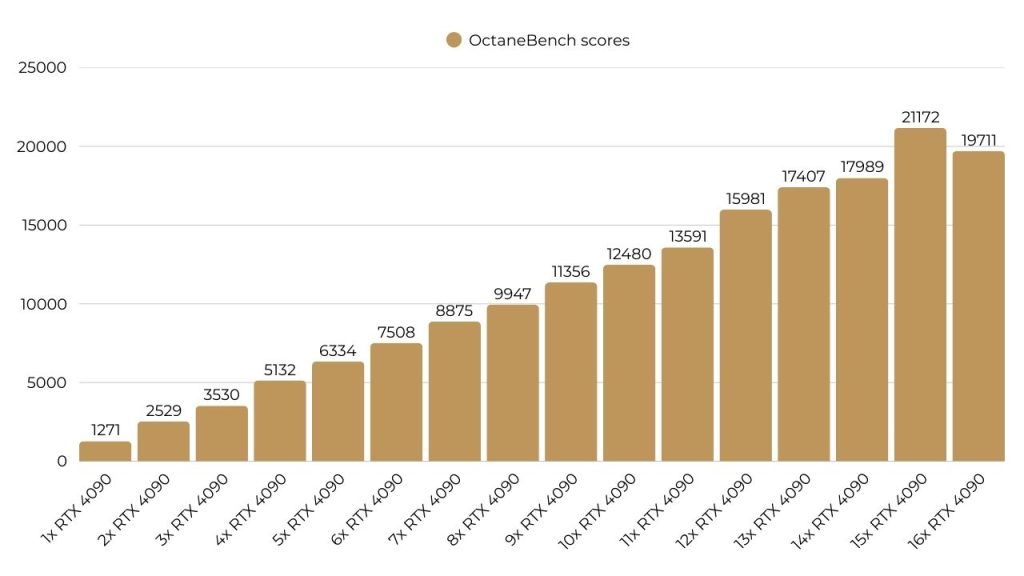
OctaneBench scores of single and multiple RTX 4090 setups
Final Thoughts
OctaneBench is a simple but powerful tool to help you measure and compare GPU rendering performance in a standardized way. It is very useful when you are building a new workstation, upgrading your GPU, or planning to use a render farm.
While it does not represent every real-world project, it offers a solid benchmark for estimating how fast your system can handle 3D rendering tasks. Knowing your OctaneBench score helps you make better decisions for freelancers, studios, and tech-savvy artists alike.
So if you have not already, give it a try. It is quick to run, free to use, and might just help you get the most out of your creative setup.
FAQ: Octane Render Benchmark
1. Is OctaneBench free to use?
Yes, OctaneBench is completely free and available for download from OTOY’s website. You don’t need a paid license of Octane Render to run the benchmark — anyone can test their GPU performance using this tool.
2. Do I need an Octane Render license to run the benchmark?
No, you don’t need an Octane license. OctaneBench is a standalone benchmarking tool, and it runs independently from the full version of Octane Render. It is designed for anyone interested in comparing GPU rendering performance.
3. Can I benchmark laptops with OctaneBench?
Absolutely. Any computer with a GPU will do. But keep in mind that thermal throttling and power limitations in laptops may result in lower scores compared to desktops with the same GPU.
4. What’s a good OctaneBench score for 4K rendering?
The higher, the better. But you can get comfortable 4K rendering with a GPU that scores from 1200+ OctaneBench scores.
5. Does VRAM affect OctaneBench performance?
Indirectly, yes. While the benchmark scenes are optimized to fit within most modern GPUs’ VRAM limits, insufficient VRAM in real projects can cause slowdowns or force fallback to system memory. So, while OctaneBench doesn’t directly scale with VRAM, having more VRAM helps ensure smooth performance on large, texture-heavy scenes.
Related posts:






No comments