GPU applications in 3D pipeline
About five or six years ago, we believed that many people still had doubts about whether GPU or CPU is more important, and whether they should use GPU in their pipeline or not. At that time, the GPU was not that powerful and the development of GPU intensive software was modest. However, if right now you still are not sure about GPU, you are definitely falling behind. GPU is not for gaming only anymore, it has unlocked new applications and possibilities in many stages of the 3D pipeline. Let us tell you more about that.
Table of Contents
What is a GPU?

GPU stands for Graphics processing unit, a specialized processor originally designed to accelerate graphics rendering.
At the beginning, translating information into images is the job of the CPU. However, as the CPU had many duties to take care of and didn’t excel at performing these kinds of tasks, the graphics accelerators were created to handle some of that specialized work that the CPU was undertaking.
The GPU now is strong enough to take over the task from the CPU. One GPU now is incredibly fast at processing complex 3D graphics. GPUs can also efficiently run other processes that involve manipulating lots of data simultaneously, which makes them useful for some applications like machine learning, video editing, and gaming applications.
What are the general phases of the 3D pipeline?
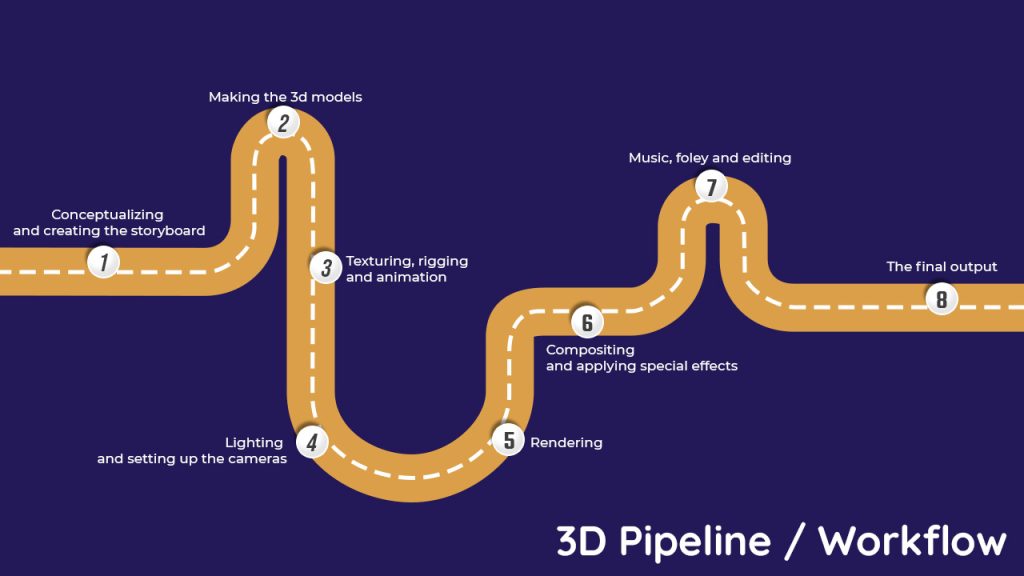
The general phases of a 3D pipeline consist of modeling, layout and animation, exporting. However, if you go deep into the pipeline, you will see there are individual steps including:
- Conceptualizing and creating the storyboard.
- Modeling.
- Texturing, rigging and animation.
- Lighting and setting up the cameras.
- Rendering.
- Compositing and VFX.
- Music, foley and editing.
- The final output.
GPU applications in 3D pipeline
1. Real-time rendering for previsualization
As said above, the GPU will do the job to process 3D images. Therefore, all works related to the images displaying will need GPU power.
For example, when you do the modeling/sculpting, it will be the CPU to do the main work for making points, edges, etc. But to actually see the model you made on the screen real-time while you work, it’s the GPU which renders it. The responsiveness and speed of model displaying in the viewport is decided by the GPU.
Of course, other steps will need the GPU too, even just 1% for you to be able to see all the changes you made with the models.
2. Texturing and the responsiveness of the viewport
When you create an object in 3D, you see in the viewport a default gray color. It’s because you haven’t applied the color and surface attributes to the 3D object. The process of wrapping the 3D models with materials, light effects, and details is 3D texturing. A high quality GPU with a big amount of VRAM can handle big textures, generate a smaller version of a texture for mip mapping. Not only the textures that are being displayed on the screen, but also every texture that might be displayed will need the GPU to do that. Imagine you spin the camera around and get lag because your PC needs to load a new texture, we bet you don’t want it to happen.
3. Faster experience with the newest lighting effects
We all know about ray tracing. Don’t tell me you haven’t heard about it. Nvidia even has a dedicated RTX series for ray tracing technology. Ray tracing is the process of tracing the paths of light rays as they bounce around a scene. It helps computers calculate the interaction and interplay much like the human eye would process real light, shadows, color and reflections, resulting in a rendered scene which looks more realistic.
Are CPUs able to compute ray traces? Of course yes, but it is super slow compared to GPU. A CPU is not able to calculate all rays simultaneously, while a GPU can do parallel processing with ease. It’s related to the number of cores. GPUs have more cores so that they can process many parallel streams of data simultaneously, no matter what that data may be.
Right now, the highest core count on offer is 64 cores from AMD, with the Threadripper 3990X. However, a RTX3090 has 10,496 Cores, and a RTX3090Ti has 10,752 cores. Can you see the difference?
4. Traditional rendering
We don’t think there is much to say here. The GPU developers have been continuously improving their product (not only for 3D, but for many fields), we can see the 3D industry’s shifting to GPU as well. Nowadays, more and more GPU-powered rendering engines are developed (like Octane, Redshift). More and more CPU-based programs have support for GPU (Arnold, Renderman). No one can ignore the fact that GPUs render much faster than CPUs do. And no one wants to be left behind (to wait for the rendering to be done) in the era of Digital Media boom, where your audience is served by many digital products in the fastest way ever.
As this is a very important part of the 3D pipeline, and is the most famous part where people tend to think GPUs are used for, there are many render farms offering their service to help you render faster. In the article of Best GPU render farms, we will introduce you to some of the best choices for it.
5. Visual Effects (VFX)
VFX in 3D consists of many simulations: particle simulation, fluid simulation, hair and fur simulation, rigid-body simulation, soft-body simulation.
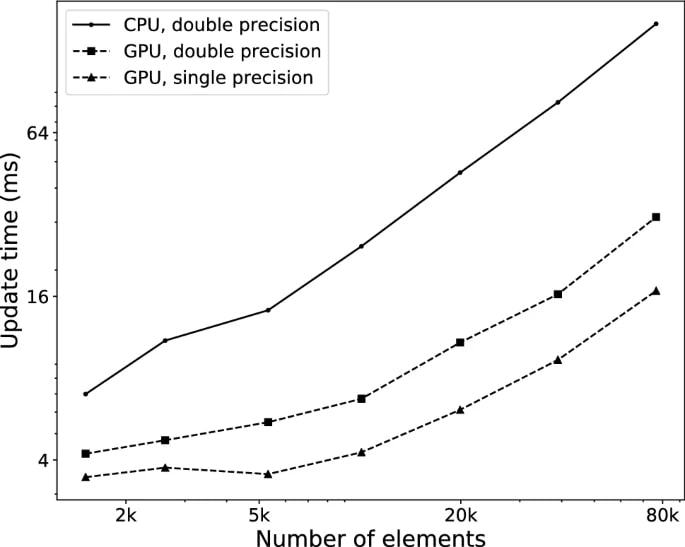
Simulation in GPUs is faster than in CPUs, because GPUs are parallel working. They can run parts of the code that are compute intensive simultaneously, enabling you to perform the simulations in a fraction of the time.
Below is the result from one simulation, comparing the execution time of 6-core Intel Core i5-9400F CPU and an Nvidia RTX 2060 GPU. As the number of elements increases, the difference between GPU and CPU grows larger. GPU, in every element size, is faster.
Final words
The CPU is important, no doubt. It tells other hardware what to do. However, as you can see, the involvement of GPUs in the 3D pipeline is significant. It’s not just simple for the rendering/exporting phase like we have always discussed (it’s the clearest application though), but you will see many other use cases, and some of them are taken for granted. We hope this article helps you to value the role of GPU more.
See more:







כנסו לאתר | 20 September, 2022
|
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges. It was really informative. Your website is extremely helpful. Thank you for sharing!