Best GPU for Architectural Rendering
Architectural rendering is an essential part of the design process, transforming abstract ideas into tangible visualizations that bring blueprints to life. Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) have become important in this digital age, revolutionizing the speed and quality of architectural rendering.
In this article, VFXRendering explains the importance of GPUs in rendering as well as recommends the best GPU for Architectural Rendering.

Table of Contents
What is Architectural Rendering?
Architectural rendering is a process of generating 2D and 3D visualizations of a planned architectural design. The goal is to accurately represent design intent by presenting a lifelike experience of how a room or building will look before it is constructed.
Benefits of Architectural Rendering
The use of 3D rendering software for architectural projects has three major advantages:
- Develop design concepts more precisely.
- Detect problems early in the development phase to cut expenses.
- Share design concepts with clients and partners.
Types of Architectural Rendering
There are typically 3 types of architectural rendering: interior, exterior, and aerial rendering.
- Interior rendering
Interior is a place that can be enhanced by details such as flooring, furnishings, and lighting. So, interior renderings depict how it will feel to work or live in that environment.
- Exterior rendering
Exterior involves light, shadowing, and reflection. And exterior rendering expresses how a building will interact with its surroundings and people.
- Aerial rendering
Aerial views provide a dynamic viewpoint, allowing for a better knowledge of landscapes, adjacent buildings, and comprehensive visualizations.
Best Architectural Rendering Software
Below are the top 3D rendering software for architectural visualization. They are all compelling and you should consider trying them out.
- Chaos V-Ray
- Lumion
- Twinmotion
- Enscape
- D5 Render
- Unreal Engine
- Corona Renderer
- Cycles Blender

Image source: Chaos V-Ray
Why do you need the Best GPU for Architectural Rendering?
Significance of GPUs in Architectural Rendering
GPUs serve as the powerhouse behind rendering, accelerating complex calculations and processing tasks necessary to create realistic visualizations of architectural designs. GPUs are designed to perform massive computational processes such as rendering fine features, textures, lighting, and shadows, as well as transforming mathematical models into photorealistic images or immersive visualizations.
With the ever-increasing complexity of architectural projects and the demand for hyper-realistic renders, GPUs have driven innovation and efficiency within the architecture field.
Importance of selecting the right GPU
Choosing the right GPU is not only a personal choice; it is a key decision that affects both efficiency and performance in your architectural rendering workflows. A well-suited GPU can drastically shorten rendering times, allowing architects and designers to iterate designs quickly and deliver visually compelling images for clients or partners.
In contrast, an inappropriate GPU may bottleneck the rendering process, prolonging timelines and compromising the quality of output. The wrong choice could restrict the capabilities of 3D rendering software, limiting the potential for intricate details or high-resolution output.
In essence, the selection of a GPU is not just about raw power; it is about aligning the specific computational needs of rendering software with the GPU’s capabilities. This will ensure a harmonious synergy that maximizes efficiency and elevates the quality of architectural visualizations.
Understanding GPU Specifications for Architectural Rendering
When selecting the best GPU for architectural rendering, understanding key specifications is important. These specifications act as the DNA of a GPU, impacting its performance and efficiency in handling rendering tasks.
Key GPU Specifications
- CUDA Cores (NVIDIA) / Stream Processors (AMD): These are the processing units responsible for executing tasks. A higher count of CUDA cores or stream processors generally correlates to enhanced parallel processing capability, enabling faster rendering of complex scenes.
- VRAM (Video Random Access Memory): VRAM is a dedicated memory for the GPU that stores textures, geometry data, and other assets used during rendering. Higher VRAM capacities allow for handling larger and more detailed scenes without compromising performance.
- Clock Speeds (Core Clock, Boost Clock): Clock speeds determine how fast the GPU can execute instructions. Higher clock speeds can lead to faster rendering times. But remember that this is not the only factor influencing performance.
- Memory Bus Width and Bandwidth: The memory bus width and bandwidth dictate how fast the GPU can access and transfer data within the VRAM. A wider bus and higher bandwidth facilitate quicker data transfer, optimizing rendering speed, especially for complex scenes with high-resolution textures.
- Compute Performance (TFLOPs): TeraFLOPs (trillions of floating-point operations per second) measure the GPU’s computational power. While higher TFLOPs can indicate better performance, it’s essential to consider this metric alongside other specifications for a holistic assessment.
Impact on Rendering Speed and Quality
These specifications collectively impact the speed and quality of architectural rendering in several ways:
- Rendering Speed: More CUDA cores/stream processors, higher VRAM, and efficient memory handling via wider bus widths and higher bandwidth directly contribute to faster rendering. They enable the GPU to handle complex calculations and store larger data sets, which results in quicker render times.
- Rendering Quality: The quality of output is as important as the rendering speed. Higher VRAM capacities ensure that intricate details, high-resolution textures, and complex scenes are rendered without compromising on quality. Additionally, efficient processing via CUDA cores/stream processors helps maintain accuracy in lighting, shadows, and reflections, enhancing the overall visual quality.
Best GPU for Architectural Rendering
After understanding the key GPU specifications, we know that choosing the best GPU for architectural rendering involves a balance between raw power, VRAM capacity, and compatibility with rendering software. Here are some top-performing GPUs renowned for their prowess in handling rendering tasks:
NVIDIA GPUs
1. NVIDIA GeForce RTX 30 & 40 Series
- Overview: Renowned for their exceptional performance in gaming, the RTX 30 & 40 series GPUs, such as RTX 3090 and RTX 4090, showcase remarkable capabilities in architectural rendering.
- Rendering Capabilities: With a high count of CUDA cores and substantial VRAM, these GPUs handle complex scenes and high-resolution textures with ease, significantly reducing rendering times.
- Pros: Exceptional performance-to-price ratio, suitable for small to mid-sized architectural firms or individual designers seeking high rendering capabilities.
- Cons: Limited VRAM compared to professional workstation GPUs.
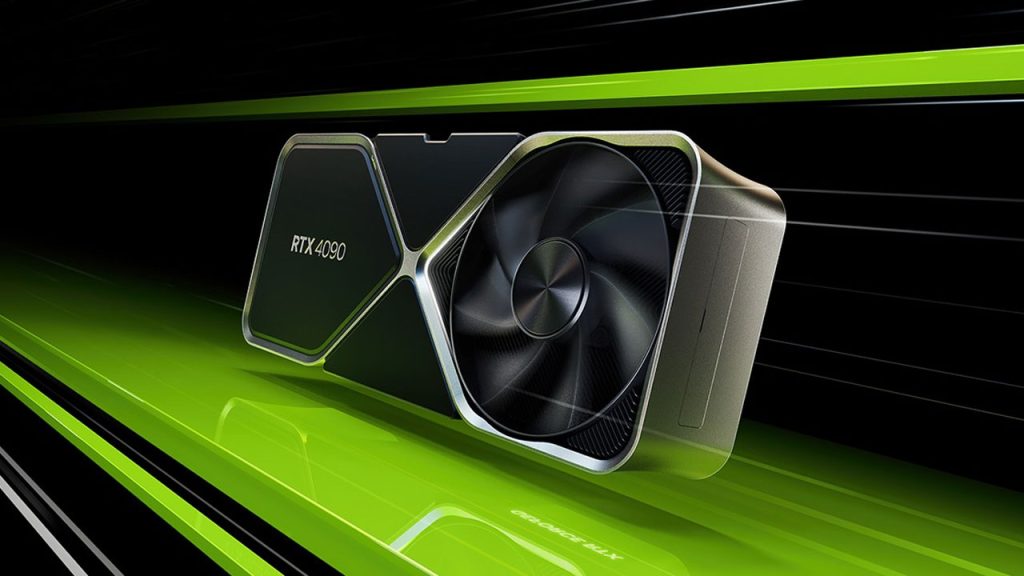

Image source: NVIDIA
2. NVIDIA RTX & NVIDIA Quadro RTX Series
- Overview: Tailored specifically for professional workstations, NVIDIA RTX GPUs (such as RTX 6000, RTX A6000) and Quadro RTX GPUs (such as Quadro RTX 5000, Quadro RTX 8000) excel in rendering complex architectural models and high-fidelity scenes.
- Rendering Capabilities: These GPUs offer massive VRAM capacities and specialized drivers optimized for professional applications, ensuring stability and reliability in demanding rendering tasks.
- Pros: Extensive VRAM, certified drivers for professional software, ECC memory support for error-free calculations.
- Cons: Higher price point, primarily suited for larger architectural firms or professionals with advanced rendering needs.
AMD GPUs
AMD Radeon RX 6000 Series
- Overview: AMD’s RX 6000 series GPUs, such as the Radeon RX 6800 XT and RX 7800 XT, compete fiercely with NVIDIA counterparts in rendering performance.
- Rendering Capabilities: Equipped with a substantial number of compute units and ample VRAM, these GPUs handle rendering tasks efficiently, offering a viable alternative for architectural visualization.
- Pros: Competitive performance, potentially more cost-effective compared to equivalent NVIDIA models.
- Cons: May lack some specialized features found in NVIDIA’s professional workstation GPUs.
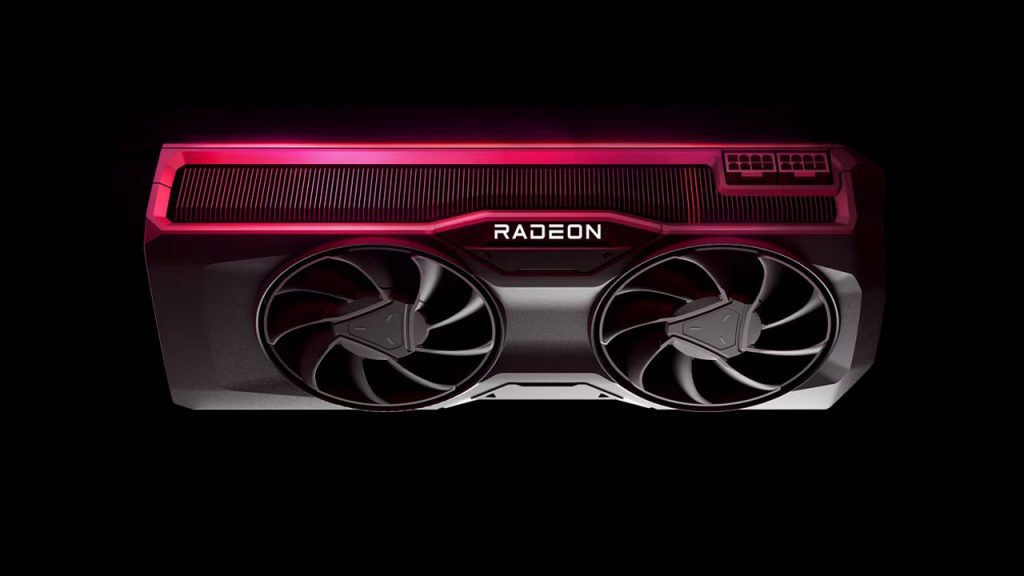

Image source: AMD
Conclusion
However, selecting the best GPU for architectural rendering from above often boils down to specific requirements, budget considerations, and compatibility with rendering software. Also, the choice between consumer-grade gaming GPUs and professional workstation GPUs is determined by the size of projects, rendering complexity, and some other factors.
By using the best GPU for architectural rendering for your projects, you can balance both speed and quality to achieve optimal results.
See more:







No comments