Should you choose Vray CPU vs GPU?
Vray users may ask themselves that should they choose Vray CPU vs GPU rendering. How are they different? VFXRendering will answer the difference between those two render engines, and help you to select the right one.

Table of Contents
Overview
Vray is a biased CGI rendering software developed by Chaos – a Bulgaria-based software company. Other than being a standalone application, this render engine also has plug-ins for a bunch of 3D software. They are 3ds Max, Maya, SketchUp, Rhino, Revit, Cinema 4D, Houdini, Unreal Engine, Nuke, Blender, Modo and Katana. Not only that, Vray is widely used for visualizations and computer graphics in various industries such as media, entertainment, film and video game production, industrial design, product design, and architecture.
Vray was originally created to work with the CPU. Later, together with the trends in graphics hardware, Chaos released Vray RT which allows artists to use GPU to create photo-realistic renders. Until now, you are able to use Vray CPU (or just Vray), Vray GPU, or Vray Hybrid (GPU + CPU). Although CPU rendering has been around for far longer, using GPUs will provide much more computing power in a single workstation.
Vray CPU vs GPU – What’s the difference?
Hardware
Vray CPU uses the CPU device to render images. To do that, at first, your computer needs to meet the minimum system requirements of Vray.
Vray GPU, on the other hand, makes use of the graphics card, but it also relies on the CPU to feed it with jobs. This means that CPU performance does have an influence on GPU rendering.
And we couldn’t forget hybrid rendering. The Vray GPU engine has a mode called hybrid rendering that takes advantage of both the CPU and GPU hardware. In this manner, the rendering performance benefits from all of your workstation’s devices.

Image Credit: AMD
Performance: Vray CPU vs GPU
The fact that Vray GPU uses multiple GPUs that are installed on a single workstation is a significant benefit. In contrast to CPUs installed on a multi-socket motherboard, adding extra GPUs is simple with affordable cost. Additionally, Vray GPU scales performance with GPUs almost linearly. For instance, two similar GPUs are expected to have faster render speeds as twice as those of one GPU. The Vray GPU rendering engine uses the RT Cores of NVIDIA RTX graphics cards (Turing architecture). The RT Cores increase the ray-tracing calculations and are capable of typically speeding up the rendering by 40%.
For Vray CPU, this render engine runs on NUMA configurations (dual CPU machine). However a significant update to the PC as a whole may be necessary. On the other hand, adding a second GPU is pretty easy if your motherboard has enough PCI slots.
However, Vray CPU requires less time to start rendering, while Vray GPU makes up for this in rendering speed thanks to its performance gains.
Supported Features
Vray CPU supports all Vray features while Vray GPU supports fewer features. This is because of the difference in the rendering engines’ codebase.
But this GPU renderer is fully production-ready and comes with all the necessary features. In addition, Chaos constantly adds more features for Vray GPU in each new release, bringing it closer to the Vray CPU engine.
Faster Feedback, Faster Decisions
Thanks to the performance improvement in Vray GPU, you now can receive feedback from a project more quickly. By doing this, you will make more decisions and be more creative for the same amount of time. As a result, you will spend more time being creative rather than rendering. This also means your overall rendering quality is much better.
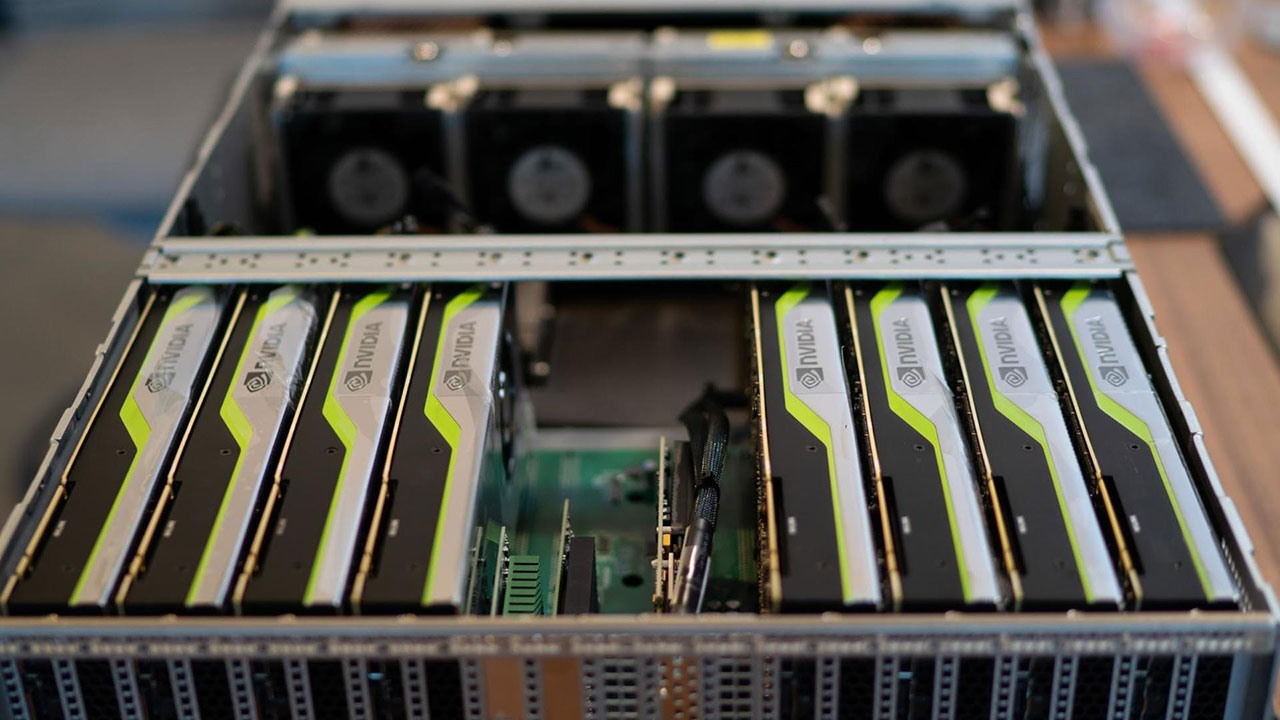

Image Credit: Chaos
Memory – Vray CPU vs GPU
Another difference when comparing Vray CPU vs GPU is the amount of memory used. Vray CPU utilizes the system memory (RAM), while Vray GPU makes use of the GPU memory (VRAM). Typical GPUs have access to 8-12GB of onboard VRAM, while CPUs can more easily access System RAM that usually counts 16-128GB in modern workstations.
It is possible to add more memory when using the CPU and RAM as long as there is a vacant slot on the workstation’s motherboard. For GPU rendering, you can easily add up GPUs to your workstation. But this does not automatically combine the VRAM of each graphics card. This functionality is only available on high-end NVIDIA GPUs with a feature called NVlink, which enables the memory of two identical graphics cards to be pooled.
The engine Vray GPU supports NVlink connections. Further, the latest version of Vray comes with an out-of-core rendering feature. When the GPU runs out of memory, this feature moves triangle meshes to the CPU’s RAM. So you don’t have to worry when rendering scenes with a lot of geometry.
Should you choose Vray CPU vs GPU?
Many Vray users might think that the only difference between Vray CPU and GPU is the type of hardware they use to run the software. So in order to compare the results, they switch from one engine to another when using the same scene. The two engines, however, work differently. Both have their benefits and drawbacks when performing rendering tasks.
Overall, Vray GPU is better at speed since GPUs can speed up the rendering process many times thanks to its massively parallel calculations. While Vray CPU is the better option to run final renders as it produces higher-quality imagery with less noise. Let’s take a look at below:
| Vray CPU | Vray GPU |
| Supports all Vray features | Production-ready has all the necessary features |
| Suitable for rendering complex scenes that need lots of memory | GPU outperforms CPU for processing parallel tasks, such as raytracing |
| Does not consume single-GPU computers’ resources while rendering | A single computer can host multiple GPUs but only have a single CPU in most cases |
| Using hardware at maximum with hybrid rendering – harnessing the computing power of both GPU and CPU devices |
That being said, Vray GPU is becoming more and more popular. Because the advancement of GPU hardware increases performance at a lesser cost.
Conclusion
To sum up, Vray offers two different render engines – Vray CPU vs GPU. Depending on what you need, you can choose a suitable Vray render engine. Usually, Vray GPU is for speed whereas Vray CPU is for quality.
See more:







No comments